| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| country | The name of the country |
| iee | Intergenerational earnings elasticity |
| gini | The Gini Coefficient |
Apply and Practice Activity
Enhancing Gatsby — an MLR
Introduction
For this activity you will build on the simple linear regression (SLR) that you fit earlier to the Gatsby Curve data.
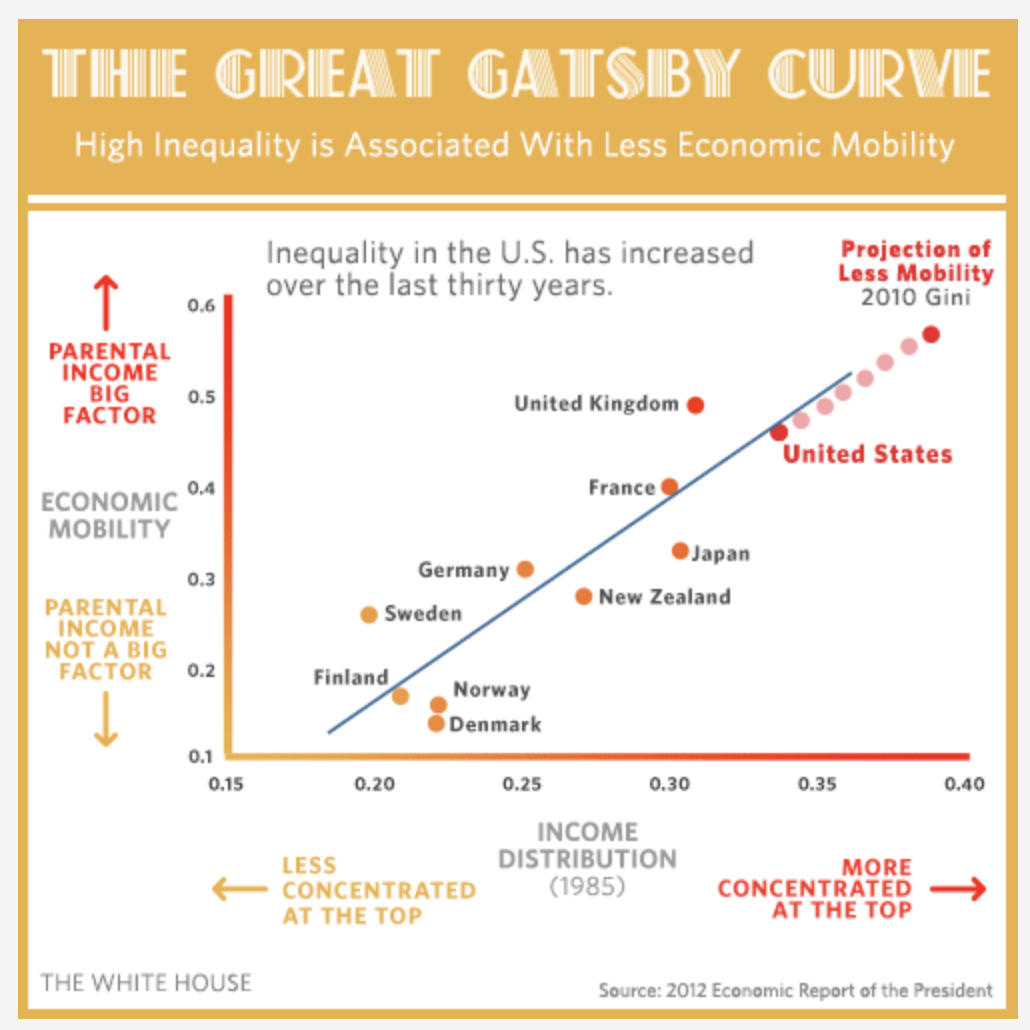
Recall that the gatsby.Rds data frame has three variables:
Please follow the steps below to complete this activity.
Step by step directions
Step 1
Navigate to the apply_and_practice_programs folder in the programs folder of the foundations project. Open up the file called gatsby.qmd.
To ensure you are working in a fresh session, close any other open tabs (save them if needed). Click the down arrow beside the Run button toward the top of your screen then click Restart R and Clear Output.
Once the .qmd file is open, add your name to the author section of the YAML metadata.
Step 2
Next we need to run the code chunks that you created in the first part of the Gatsby Apply and Practice Activity to fit the SLR. Find the down arrow beside the Run button, click on it, then choose Run All.
Step 3
Scroll to the bottom of your analysis notebook, and create a first level header labeled
# Add average parental education
Insert a code chunk.
Inside the code chunk that you created, please add a new variable called parent_ed — which represents the average years of education of parents in the country. Here’s a spreadsheet of the data we need:
| country | parent_ed |
|---|---|
| Argentina | NA |
| Australia | 10.43 |
| Brazil | 2.70 |
| Canada | 11.02 |
| Chile | 6.32 |
| China | 2.76 |
| Denmark | 10.08 |
| Finland | 8.55 |
| France | 7.49 |
| Germany | 12.51 |
| Italy | 7.81 |
| Japan | 10.88 |
| New Zealand | 12.40 |
| Norway | 10.69 |
| Pakistan | 1.28 |
| Peru | 3.81 |
| Singapore | NA |
| Spain | 4.29 |
| Sweden | 8.92 |
| Switzerland | 10.98 |
| United Kingdom | 9.16 |
| United States | 11.89 |
Make note of the two countries that are missing data for parent education.
To begin adding this variable to the data frame, copy and paste the code below into your code chunk. Study the pattern for adding the parent_ed variable to the data frame, then complete the code to add education for all countries with available data.
gatsby_ed <-
gatsby |>
mutate(parent_ed = case_when(
country == "Australia" ~ 10.43,
country == "Brazil" ~ 2.70,
country == "Canada" ~ 11.02
))Double check your data entries to make sure there are no typos. Then, click play on the code chunk. Click on the new data frame that you created (gatsby_ed) in the Environment tab to ensure that you now have the parent education scores filled in (except for the two countries with missing data — Argentina and Singapore).
Step 4
To your pipe in Step 3, add a pipe operator at the end of the last line, return to a new line, then add one final line of code to drop the countries with missing data. The additional code line is:
drop_na()
Add another pipe operator after drop_na(), and then use the mutate() function to center both gini and parent_ed at the mean in the sample. Your data frame should look like the one below. If you’re having trouble getting the code right, click on the Code tabset below.
gatsby_ed <-
gatsby_ed |>
drop_na() |>
mutate(gini.mean = gini - mean(gini),
parent_ed.mean = parent_ed - mean(parent_ed)
)Step 5
Create a second level header labeled
## Scatterplot of iee and parent_ed
Insert a code chunk.
Then create a scatter plot of parent_ed (on the x-axis) and iee (on the y-axis). Request the best fit line, and label the points with the country name. This graph will be very similar to the graph that you created earlier for gini and iee in the original activity.
Write a few sentences to describe the graph.
Step 6
Add a second level header called
## Fit a MLR
Insert a code chunk, then refit the simple linear regression that we fit earlier, regressing iee on gini.mean, but now on the data frame that dropped the two countries with missing data on parent_ed (the variable we will consider next). This is important because in comparing two nested models (where one model — the SLR — is a subset of another fuller model – the MLR — it is important that the same cases (i.e., countries in this case) are included).
Use the tidy() function to request the estimates of the intercept and slope. Use the glance() function to request the \(R^2\) and sigma. Study the output.
Then, below the code to fit the first model, fit a second model, a multiple linear regression model, that adds parent_ed.mean. Regress iee on gini.mean and parent_ed.mean. Use the tidy() function to request the estimates of the intercept and slopes. Use the glance() function to request the \(R^2\) and sigma. Use augment() to request the .fitted and .resid scores.
Write a paragraph to interpret the intercept and slopes from the model output. Describe and interpret the \(R^2\), and reflect on the change in the slope for gini from the first model (without parent_ed) to the second model (with parent_ed). Last, reflect on the change in the \(R^2\) between these two models.
Step 7
Finalize and submit.
Now that you’ve completed all tasks, to help ensure reproducibility, click the down arrow beside the Run button toward the top of your screen then click Restart R and Clear Output. Scroll through your notebook and see that all of the output is now gone. Now, click the down arrow beside the Run button again, then click Restart R and Run All Chunks. Scroll through the file and make sure that everything ran as you would expect. You will find a red bar on the side of a code chunk if an error has occurred. Taking this step ensures that all code chunks are running from top to bottom, in the intended sequence, and producing output that will be reproduced the next time you work on this project.
Now that all code chunks are working as you’d like, click Render. This will create an .html output of your report. Scroll through to make sure everything is correct. The .html output file will be saved along side the corresponding .qmd notebook file.
Follow the directions on Canvas for the Apply and Practice Assignment entitled “Gatsby MLR Apply and Practice Activity” to get credit for completing this assignment.